About our water source

Namaste Spring Water is from a Federally Protected Spring in Palomar Mountain San Diego. Our 100% genuine spring water is naturally filtered through the mountain’s layers and emerges crystal clear at its source.

Naturally occurring nutritional components
Calcium (Ca) 12mg/L
Magnesium (Mg) 4.1 mg/L
Potassium (K) 2mg/L
Hardness 47mg/L
TDS* 84 ppm*
pH 7.4
*TDS = Total Dissolved Solids Total dissolved solids (tds) is the sum total of all the minerals in water.*ppm = parts per million.
Namaste water is an extraordinary provider of premium spring water which takes up particular market position due to its pure (ph-neutral) water quality, its ingredients and its purity. We are very pleased to have found a spring which is federally protected and that supasses FDA regulations for purity and it is one of the freshest, best tasting spring water in southern California!

In order to preserve the purity of the crystal clear spring water, the water is filled directly at the source in a careful manner into stainless steel holding tanks and than transported to our bottling plant enabling it to maintain its origin, its natural energy and its particular character which it has developed during its long journey.
Below you can read about the water purification process in detail and we can assure you that we are committed to excellence throughout every step of our purification process which is considered to be the finest available in the industry.
Water purification process
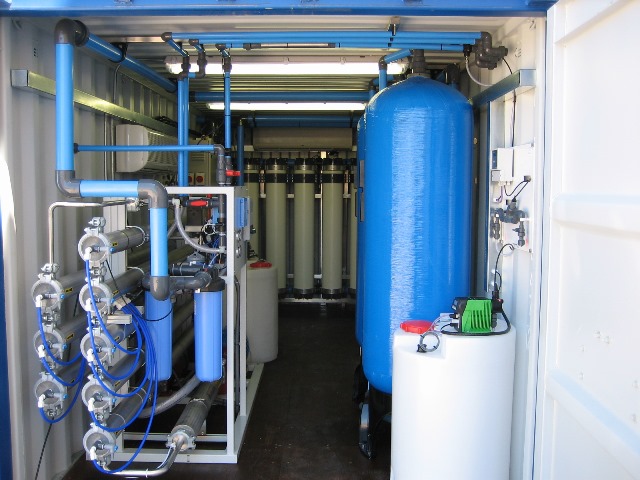

Reverse osmosis water
The water system pre-treats the incoming raw water by passing it through a Granular Activated Carbon Filter. Followed by a set of water softeners. The water then travels through a 20 micron Particle Filter Unit before entering the Reverse Osmosis Unit (RO). The RO product water is stored in the RO Storage Tanks. When selected for bottling, the RO Water becomes the source water for drinking water products.
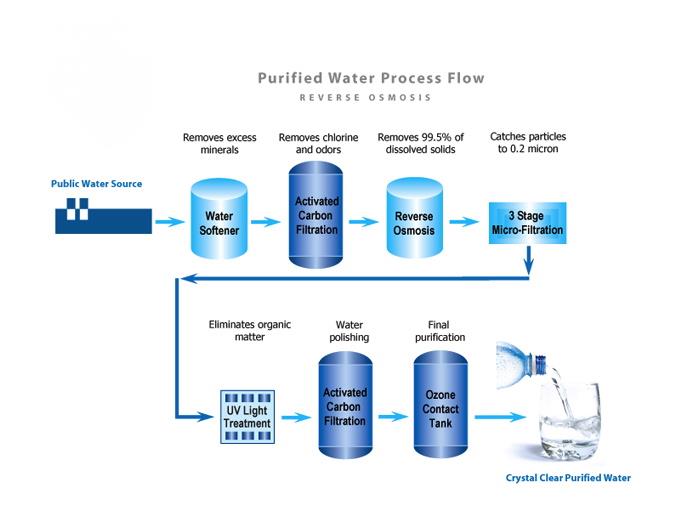
Final filter unit
A multi‑element particle filter is provided prior to the ozonation injection system. These 5, 1 and 0.2 micron nominal depth filters are placed downstream of the storage tank to assure the removal of any suspended particles from the final product water. Small particles can be detected in clear PET bottles and may cause customer complaints. The final filter unit assures that any particles in the storage tank (down to 0.2 micron) are removed. For comparison, a human hair is about 200 microns or 50 millionths of a meter.
The filter elements are housed in a stainless steel multi‑element canister to allow for proper flow at a minimum pressure drop. The elements are made with compressed fibers of polypropylene that form a torturous path for the particles to travel through. This path entraps the particles leaving the cleaned water to pass. These types of filters come in a variety of micron sizes, however a 1 micron nominal filter rates (removal of 99.90 of particles 1 micron or larger) elements offers sufficient protection at an affordable cost.
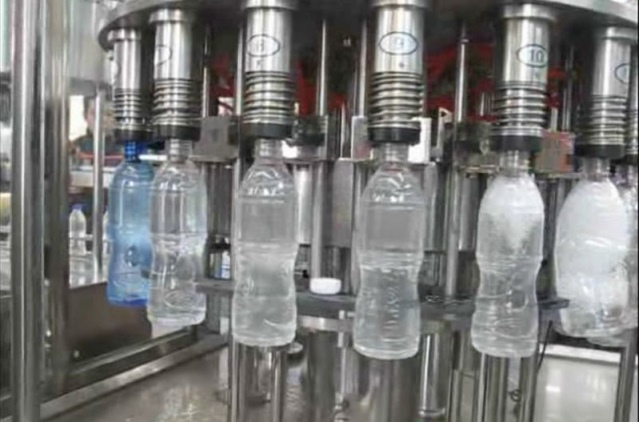

The ozonation system
Just prior to bottling, the water is ozonated to remove bacteria. The ozonation system consists of an oxygen supply, an ozone generator, an injection assembly, and a contact assembly. Ozone gas is injected into the base of the contact tank forcing continual contact with the water. The contact assembly allows the ozone to mix completely with the water and remain in contact for 30 to 60 minutes. The dissolved ozone then has a long period to react with the water before being sent to the filler. Ozonated water is then transferred to the fillers. Ozonated water directed to the filler passes through a pipeline to the Filler units located in the bottling clean room. During start‑up, the pipeline must be purged of any “old”‑product so that the water meets specification. A drain valve is located on the filler reservoir to accomplish this.

Ozone is an unstable, colorless gas that is a powerful oxidizer and potent germicide. Ozone has a much higher potential than other disinfectants and is some 3000 times faster than chlorine at killing bacteria. Chemically, ozone consists of 3 atoms of oxygen (oxygen gas has only 2 atoms). The 3 oxygen atoms are very unstable. They quickly decompose to normal oxygen plus 1 free oxygen atom. This extra oxygen is responsible for much of the oxidizing effect of the ozone gas. Ozone can be used to remove iron, manganese, color, taste, odors, and organics from water.
Several variables determine the effectiveness of ozone’s destruction of microorganisms. These include contact time, ozone gas concentration, and dose rate. As with chlorination, most waters have an ozone demand. This demand must be met to achieve a free residual. For example, 2 mg/l of ozone may be added to the water to get a 0.2mg/l concentration in the bottle. The ozone concentration in the contact assembly may actually decrease to the 0.5-mg/l level before exiting the contact assembly.
Ozone residual can also depend on time and temperature. This means that in cold water ozone residual can be maintained for several days. If left to ambient air or warm temp the ozone can dissipate much faster. The ozone residual shall be kept between 0.1‑0.4 ppm in the bottle immediately after filling.

